CBD 101: Beginner Guide to CBD Oil
Public opinion about cannabis is changing faster than ever, all thanks to a simple compound known as CBD.
But what is CBD? Why is it so popular?
This comprehensive guide covers all the basics of CBD. We’ll cover how CBD works, how much you should take, and how to get the most out of it.
Whether you’re a regular consumer or brand new to CBD, our guide covers everything you need to know.
This is a really big topic, so let’s get started.
A Primer on CBD & CBD Oil
CBD stands for cannabidiol — a completely non-psychoactive, naturally-occurring compound unique to cannabis plants. It’s become extremely popular in recent years as a natural health booster with little to no side effects typical to common OTC medications.
CBD oil can be extracted from hemp and marijuana. Both plants are the same species of plant but have completely different growth patterns. Hemp produces virtually none of the psychoactive THC molecules common in marijuana.
It’s this key difference that allows CBD oils made from hemp plants for sale legally, while CBD oils made from marijuana remain a restricted substance.
CBD works primarily by interacting with the endocannabinoid system — an important network in the body that relies on naturally produced cannabinoids (such as anandamide and 2-AG)to maintain the balance between various organ systems.
Essentially, the endocannabinoid system keeps the body in balance through a process called homeostasis.
Ever since CBD was introduced to mainstream media, the cannabis industry has entered the age of renaissance.
The Origins of CBD Oil

Cannabis is one of the earliest agricultural crops, with first records of use dating back 10,000 years.
Since then, people have used cannabis for food, textiles, and medicine for centuries.
Traditionally, hemp fibers were used to make ropes and fabrics. Seeds served mainly nutrition, and the flowers and resin were used for medical purposes.
Cannabis was a highly regarded medicine among some of the greatest civilizations of the past — from China to Egypt.
As humans began to discover that different species of cannabis have different purposes, they started cultivating both forms of the plant — hemp and marijuana.
Hemp plants are usually tall, thin, and fluffy. Marijuana plants are more like bushes with their short and bulky structure. Marijuana also produces more resin than hemp, which is where most of the active medical constituents of the plant are stored.
The first records of hemp oil come from 2737 BC when the Chinese emperor Shen-Nung used it topically for rashes and irritated skin. He also used cannabis tea for conditions like gout and indigestion.
Queen Victoria’s doctor, J.R. Reynolds prescribed her a strain of marijuana high in CBD to help manage menstrual cramps.
At the beginning of the 20th century, particularly throughout North America, marijuana plants were bred to contain high concentrations of THC for stronger psychoactive effects and greater medical activity.
Traditional cannabis culture fell into shambles during the 1930s at the start of the marijuana prohibition.
Following the War on Drugs in the 1980s, President Reagan’s administration invested millions of dollars into research intending to back the government’s claims about the negative impact of marijuana on the brain and cognitive function.
Not only did those studies not help them meet their goals, but they also resulted in the initial discovery of the endocannabinoid system in humans.
Today, scientists are preparing to expand research on CBD, THC, and other cannabinoids to understand how they work, what their limitations are, and how they can benefit society as medicine, textiles, and various other industries.
Today, there’s a lot of money in the cannabis industry.
The CBD market’s worth in the United States is estimated to hit $4.3 billion by 2026.
What Does CBD Oil Look Like?
CBD oil is a thick viscous oil that can range from clear to dark-green in color.
It’s a herbal extract designed for sublingual (under the tongue) consumption, or by swallowing the liquid.
Carrier oil such as hemp seed oil or MCT oil is an essential ingredient in CBD oil to make it easier to use. CBD in its natural form is a white powdered crystal that brings incredible potency even with small doses. By diluting the CBD and other active ingredients in an oil it becomes much easier to measure the ideal doses.
The carrier oil choice affects the appearance of the oil, with vegetable oils like olive oil having a darker color than more refined carrier oils like MCT or fractionated coconut oils.
How is CBD Oil Used?
CBD oil is very easy to use.
All you have to do is squeeze the dropper of your bottle, measure out your dose of CBD, and place the liquid under your tongue for 30-60 seconds before swallowing.
It’s THAT simple.
Alternatively, you can add the oil to your juice, tea, or any other drink.
The most complicated part is determining how much oil to measure for your dose. This can vary from one person to the next and will depend on the potency of the oil.
Most people find a 10 or 20 mg dose of CBD oil to be ideal — which works out to around 10 or 15 drops of a standard 1000 mg CBD oil.
How to Distinguish High-Quality from Poor-Quality CBD Oil
There’s a large degree of difference when it comes to the quality of CBD oil.
A decent CBD oil should have a strong hemp flavor and can range from clear to dark green in color. The viscosity of the oil increases along with the potency of CBD.
No CBD oil should have foul smells, black colors, or chunks of plant matter. If you find anything like this, return the product to the manufacturer and find another brand.
CBD Extraction: How CBD Oil is Made
CBD extraction is very similar to other plant extractions.
The majority of CBD oils are extracted from hemp plants instead of marijuana. If you remember what we discussed above, hemp plants contain little to no THC, while marijuana can range from low to very high concentrations of this psychoactive compound.
Only CBD oils made from hemp are considered legal across the United States. Only 11 states allow oils to be made from marijuana plants without a medical license.
There are two common methods for CBD extraction:
1. Alcohol Extraction
Any fat-soluble substance also dissolves in alcohol. This means that you can efficiently extract CBD and cannabis terpenes from the plant using an alcohol such as ethanol or methanol. This is one of the oldest extraction methods still used today.
2. Supercritical CO2 Extraction
Most reputable companies use CO2 to extract their hemp. It’s considered the “gold standard”.
CO2 extraction involves passing the gas through several temperature-controlled chambers under high pressure to cause CBD to enter a supercritical state. While in this phase, CO2 has both the qualities of gas and liquid. It also gains extremely efficient solvent properties that pull the active chemicals from the plant material.
This first extract contains all the phytochemicals in the hemp plant. We refer to this as a full-spectrum extract.
Some companies do an extra extraction step to further isolate the CBD from the rest of the hemp-derived chemicals.
The Difference Between CBD from Hemp and Marijuana

CBD is CBD no matter the source, but CBD oil made from hemp is different from the one sourced from marijuana. Here we explain these differences, highlighting the chemical profile of both types of CBD oil.
Hemp-derived CBD
Hemp plants are cultivated specifically for their higher CBD content and low levels of THC (usually around 0.3% or below). Since CBD is non-intoxicating, hemp-derived CBD oil allows you to benefit from the CBD without experiencing its psychoactive side effects.
Marijuana-derived CBD
Marijuana is any Cannabis sativa plant that contains more than the federal limit of 0.3% THC in dried weight.
In most countries, marijuana is still a controlled substance. The possession, cultivation, and distribution of marijuana can get you charged with a criminal offense.
Currently, CBD oil from marijuana is legal in 11 US states for recreational use and in 33 states for medical use.
CBD Oil Dosage Instructions: How Much CBD Should I Take?
If you want raw numbers and dosage ranges for specific cases, you won’t find them here.
That’s because there is no one-size-fits-all CBD dosage.
CBD affects everyone differently.
The key to figuring out your effective CBD dose is to calculate the potency of your CBD oil first.
CBD oil usually comes with a dropper. One full dropper equals 1 mL of oil, which is about 30 drops.
So, for example, if you have a 500 mg CBD oil in a 30 mL (1 oz) bottle, there will be about 16.6 mg of CBD in each mL of the liquid.
An ounce (30 mL) of a 1000 mg bottle will have approximately 33.3 mg of CBD in 1 mL.
This is the basic method for calculating your starting dose. It’s recommended that you start with a very low dose and build up gradually over time.
Start with 2 mg and add 2 mg to your dose each time until you find a level that suits your health goals.
For some people the ideal dose will remain at 2 mg, while others need much larger doses of around 50 mg to get the effects they’re looking for — everybody is different.
Why Does CBD Work Differently for Everyone?
The dosage of CBD will vary from person to person. That’s because several factors affect the way CBD interacts with your body, including:
- Gender
- Age
- Weight
- Metabolism
- Genetic predispositions
- Biochemistry
- Underlying health conditions
Any of these factors and their combinations can increase or decrease your sensitivity to CBD and other hemp derivatives.
Full-spectrum CBD Oil vs. Isolate: Which One is Better?
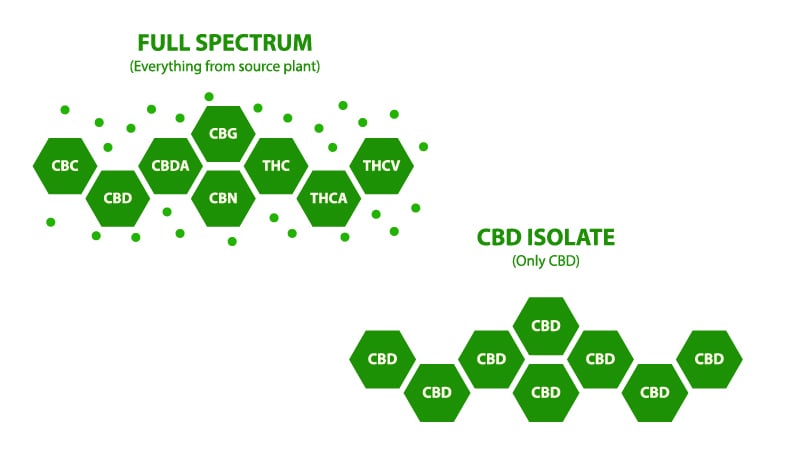
When browsing through different CBD products online, you may notice that some of them are labeled as “CBD isolate” or “THC-free” while others are listed as “full-spectrum CBD.”
Let’s take a look at the main differences between these two forms of cannabidiol.
1. Full-Spectrum CBD Oil
To put it simply, full-spectrum CBD refers to a product that contains all the naturally-produced chemicals in the hemp plants. This includes, but is not limited to CBD as well as other cannabinoids like CBC, CBG, CBN, and a long list of terpenes and related chemicals.
There are over 400 compounds in hemp and marijuana, including cannabinoids (with traces of THC below 0.3%), terpenes, flavonoids, vitamins, and trace minerals.
Many experts agree that full-spectrum CBD oil is more effective than isolate, which scientists link to a phenomenon known as “the entourage effect.”
The concept of the entourage effect — or whole-plant synergy — is based on the theory that cannabinoids, terpenes, and other molecules from the plant can enhance each other’s effects. That’s why lower doses of full-spectrum extracts remain efficacy where isolates fail to deliver desired effects.
2. CBD Isolate Oil
CBD isolate is exactly what it sounds like — pure CBD that has been isolated from other cannabinoids, terpenes, flavonoids, and other compounds.
While isolates are generally weaker than the same dose in a full-spectrum product, there are some advantages to this extract type.
Here are 4 reasons why you may consider buying CBD isolate:
- Isolates offer a higher dose of CBD per serving
- CBD isolates contain 0% THC
- You can precisely control the potency of CBD in isolates
- Isolate is taste- and odor-free; you can add it to food and drinks and use the benefits of CBD without the unpleasant taste of natural CBD oil.
Where to Buy CBD Oil
CBD oil is widely available throughout the United States thanks to the 2018 Farm Bill. There are three places where you can buy CBD products:
1. Buy CBD Oil Online
The majority of CBD products are sold online, which is how we recommend searching for CBD oil.
Buying online is safe, easy, and convenient. Once you’ve made up your mind and chosen your products, they will be shipped to your doors within 1-3 business days on average. You can enter loyalty programs, use seasonal deals, or buy in bulk to save money on your supplies.
Not to mention that it’s easier to research your potential CBD oil vendor so that you can decide whether you can trust them or not.
2. Buy CBD Oil from Dispensaries
If you prefer buying CBD oil locally, you can try to get your products locally. CBD is sold in dispensaries in many different forms.
Dispensaries allow users to buy CBD oil in person, where you can choose between products from hemp and marijuana. However, if your state doesn’t allow the recreational use of cannabis, you’re going to need a medical marijuana card or a doctor’s recommendation to buy CBD oil with a higher THC content.
3. Head Shops
You can find many hemp-derived CBD products in local head shops or wellness stores. Similar to dispensaries, these types of stores supply people not only with CBD oil but also with a wide range of hemp accessories.
Unfortunately, head shops aren’t regulated, so the owner of the store can actually sell anything they consider “good quality”, even if it’s far from that.
As a result, there are many head shops selling untested CBD oil just to lure unaware customers and earn quick money on their lack of knowledge.
Key Takeaways on CBD Oil
CBD oil has many well-documented health benefits. It helps regulate the vital functions of your body, brings a sense of balance to your mind, and improves regeneration. When incorporated into an active lifestyle and healthy diet, it can have a dramatically positive impact on your health.
It’s no wonder so many people take CBD oil today. After all, cannabis has a long record of historical use, tracing back several millennia before the common era.
Nevertheless, please note that CBD is not a panacea. It’s not even an officially approved drug. The FDA has classified hemp-derived CBD as a health supplement, so if you suffer from a medical condition or are taking prescription drugs, discuss your plans with your doctor before you decide to buy CBD oil. CBD may have a negative interaction with certain medications.
Let us know in the comment section below how CBD oil has helped you — let’s raise awareness about this cannabinoid and how it can help people feel better!
